Scribe Post #5
Learning Target:
Solve inequalities using using physical models, paper and pencil, tables, and graphs.
How it Works, What it is:
Here is an example problem: x-7 < 3 This may look confusing, but the answer lies in finding all the possible numbers that can represent the variable x. Since < means that the right side of the equation is greater, we know that x has to be less than 10 because 9-7=2, 8-7=1, and so on. If you do 10-7, 3 still wouldn't be greater, just equal. The equation can be written like this:
x - 7 <3
bring down the x +7 +7 add 7 to each number
_________
0 10
x < 10
You can also do this on number lines, which makes things a heck of a lot easier. For example, x<4 has to be any number less than 4. This number line shows this by putting an arrow leading left from four to up to negative infinity. This graph shows that any number less than 4 could represent x.

Here is another example: -2 < x ≤ 4

(Note that this is a different level. Click here for more info on that kind of inequality, and the regular kind.)
If you really want to search this topic more, then this page is for you!
 You've got it now!
You've got it now!
Scribe Post #4
Learning Target
Know how to use a coordinate plane and know what it is.
Example
 If I want to find (2,2), I go across the X-axis (the horizontal line) to 2, then go down the Y-axis (the vertical line) to 2. I can do this in any quadrant (the boxes made by the intersecting axises) and I can go to the numbers below and to the left of 0 to get negatives. Any numbers on the X-axis will have the Y-coordinate of 0, and visa-versa.
If I want to find (2,2), I go across the X-axis (the horizontal line) to 2, then go down the Y-axis (the vertical line) to 2. I can do this in any quadrant (the boxes made by the intersecting axises) and I can go to the numbers below and to the left of 0 to get negatives. Any numbers on the X-axis will have the Y-coordinate of 0, and visa-versa.
The Kiwi Bird
There are three types of kiwis: the kiwi as in a human who was born in New Zealand, the kiwi as in the fruit, and of course, the bird.



This is not a Kiwi Bird. Neither is this. This is a kiwi bird!
There are 4 types of kiwi birds.
The Brown Kiwi:

The Great Spotted Kiwi:

The Little Spotted Kiwi:

The Tokoeka Kiwi:

For more information on the 4 types of kiwis, click here.
The life cycle of a kiwi:
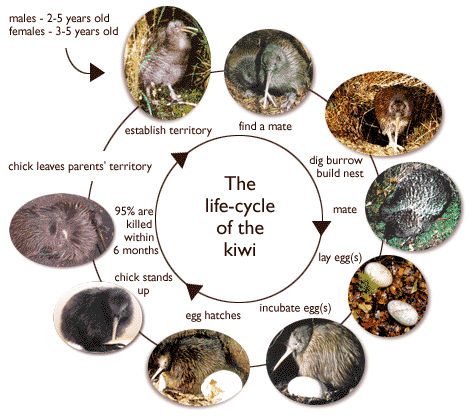
Kiwis are unique because:
1)They are the only birds to have nostrils at the tip of their beak. This helps them forage for insects to eat.
2)They are very unusual birds because their feathers are like hair, their wings are about 2 inches long (they are flightless), and they are nocturnal.
3)They have the largest eggs of any bird in proportion to their body size. The kiwi is about the size of a chicken and their egg is about the size of an ostrich egg, but a bit smaller.

A kiwi's nostrils help it find food deep in the ground.
posted by Jonathan Rutter (a kiwi!)
Scribe Post #3
Learning Target
Add and subtract with fractions with unlike denominators and justify your solutions using manipulatives and mathematical reasoning.
Sample Problem
6/7+5/8=x
6/7 - 48/56
5/8 - 35/56 48+35=83 ------ 83/56 ------ 1 27/56
Lesson
To add two fractions with unlike denominators together, you must find the Least Common Denominator (L.C.D.) by finding the smallest number that both denominators are divisable by. Then, take the number that you multiply by to get the L.C.D. and multiply it by the numerator of each fration. Those numbers are the numerators of the new fractions. Then, find the sum of the numerators and put them over the same denominator. If it is an improper fraction, subtract the denominator from the numerator and use that number as your numerator, while the denominator remains the same. Add a one to that fraction and then simplify.
To subtract two fractions with unlike denominators from each other, you must follow the same algorithm as when you add fractions with unlike denominators, but you must subtract the numerators instead of adding them. Then simplify the fraction.
Scribe Post #2
Learning Target
Use strategies to develop formulas for finding the circumference of a circle.
Sample Problem
C÷D=Π C=circumference D=Diameter Π=Pi
Lesson
To find the circumference of a circle, you can take a piece of string and wrap it around the perimeter of it once, then measure the string. To find the diameter, take the string and hold it across the widest part of the circle. This can be defined as follows: C/D. Then divide the circumference by the diameter to get Pi (however, you will not get exactly Pi, but somewhere close). Pi is the quotient.